When you have installed an SSL certificate on your website, you ensure that your visitors can reach your website securely. This security is visible to your visitors, it is shown as a lock in the address bar of your browser.
it is possible that the SSL certificate has not yet been installed correctly. Another possibility is that there is 'Mixed content' on your website. This means that files or images on your website are still being called via HTTP, while your website as a whole is accessible via HTTPS.
Make sure the SSL certificate is installed correctly
To make your website accessible securely and thus show a lock in the address bar, it is first of all important that the SSL certificate is installed correctly. Use the article below to install the SSL certificate of your choice on your website.
Once the SSL certificate is installed on your website, you should see a lock in the address bar of your browser.
Mixed content
Do you not see a lock in the address bar of your browser after installing your SSL certificate? Then your website most likely contains Mixed content. This means that some of the content of your website can still be reached via HTTP instead of HTTPS. When (part of) the content of your website is accessible via HTTP, the data that your visitors send via your website may not be encrypted. This would allow malicious parties to intercept or modify this data.
For that reason, in the case of Mixed content, no lock is shown in the address bar;after all, the connection to your website is not completely secure. It is therefore important that you make the content of your website fully accessible via HTTPS as quickly as possible.
Open your browser's console
To check whether Mixed content is present on your website, proceed as follows:
- Open the website in the address bar of your browser.
- Press F12, or for Mac users press [ cmd + opt + i ].
- Click the 'Console' tab.
If you don't see any content in this tab yet, please refresh the page.You have now opened the 'Console' of your browser. Here you can immediately see which links in your website are still accessible via HTTP instead of HTTPS.
Below is an example of the Console, in which the secure page https://ssl-voorbeeld.nl/voorbeeld-pagina/ is delivered over HTTPS. However, this page requests an image via HTTP. This creates Mixed content on the website, which makes the website considered unsafe.
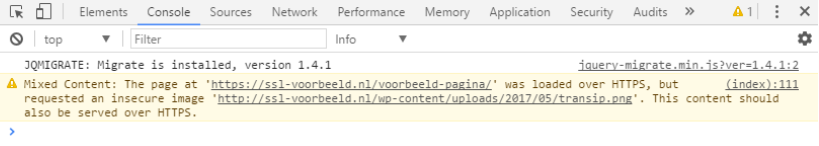
There are several ways to solve this. We recommend that you look up the location of the relevant link in the configuration of your website and then manually change it from HTTP to HTTPS.
If you use a WordPress website or another CMS, it is often sufficient to delete the image via the management environment of your CMS and then upload it again.
If you use WordPress, there are plenty of plugins that can convert the HTTP links to HTTPS. Use the search term 'Mixed Content' in the overview of plug-ins to see a list of relevant plug-ins. Please note that such plugins can affect the loading time of your website.
After you have successfully transferred the links with HTTP to HTTPS, your website will now show a lock in the address bar.
In this article we have explained what to do when you do not see a lock in your browser when navigating to your website.




