Block Storage allows you to add an extra disk with considerable storage capacity to your VPS. This is for example useful for data storage such as media files or back-ups.
Follow the steps in this article to order Block Storage and use it on your Linux VPS. Should you already have a Block Storage disk, jump streight to configuring your Block Storage.
- This article applies to a Linux VPS. For Windows, check our article about Block Storage for your Windows VPS.
- Please note that using LVM may add additional complexities, especially when moving a Block Storage from one VPS to another. As such we recommend using the steps in this guide (ext4).
- Data transfer between your VPS and Block Storage does not count towards your VPS' monthly data traffic limit.
- If you use an existing Block Storage, please note that it can only be added to a VPS in the same availability zone.
Ordering Block Storage
Step 1
In your control panel navigate to the tab 'VPS'.
Step 2
Scroll down to 'Order extras' and click 'Bestellen' behind 'Extra storage, up to 40TB'.
Step 3
Choose the size of the disk and whether or not you'd like to use off-site back-ups for your Block Storage disk. When you're finished, click 'Continue' and follow the remaining steps of the order process.
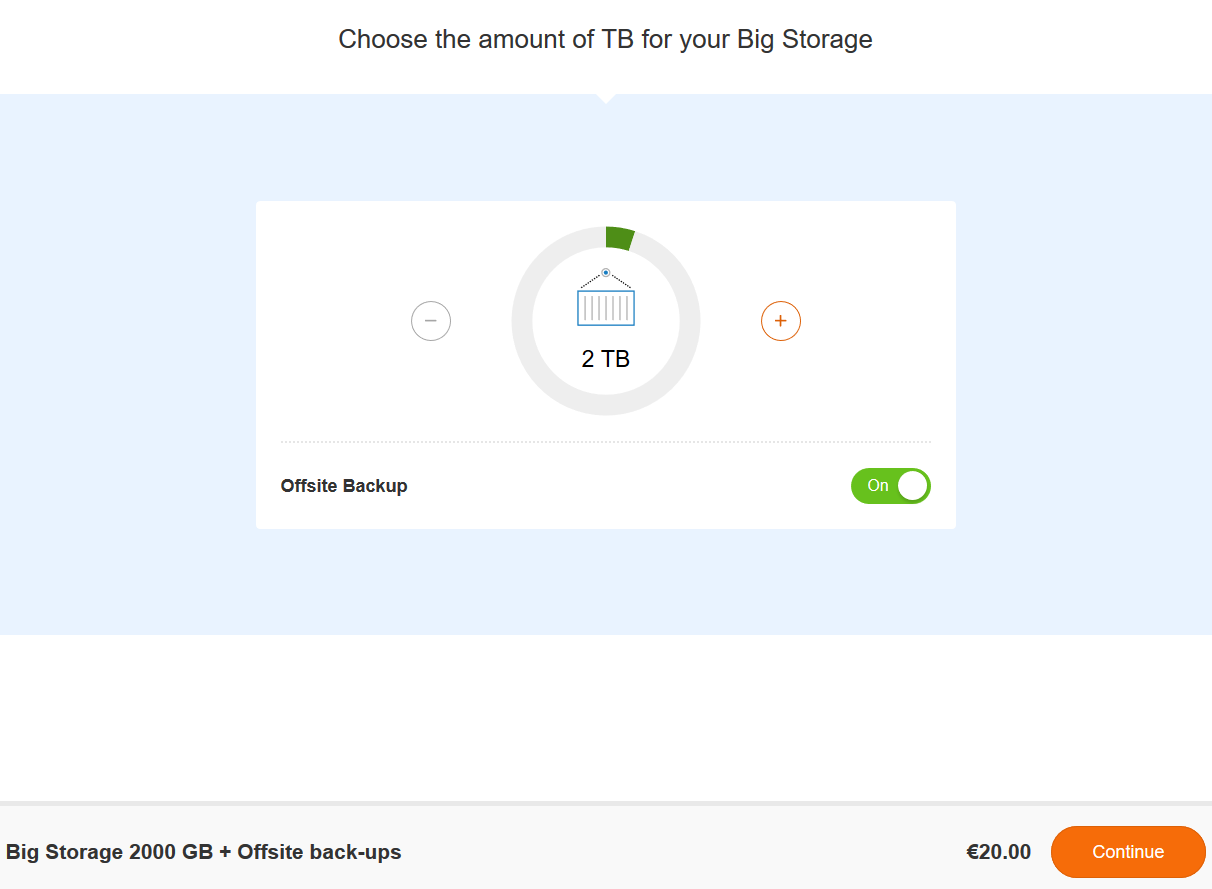
Please note that it may take a little while before your Block Storage becomes visible in your account.
Step 4
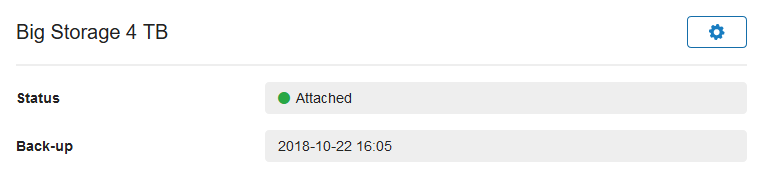
After completing the order, you're returned to your VPS overview page. Beneath the VPS console a new section called 'Block Storage X TB' will be visible. You can manage your Block Storage by clicking the cog wheel behind it.
Configuring Block Storage
Execute the steps below as a user with root rights
Step 1
Use the following command before and after the Block Storage is linked to your VPS:
lsblkThe output will look similar to this example:
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
vda 253:0 0 150G 0 disk
vda1 253:1 0 146G 0 part /
vda2 253:1 0 1K 0 part
vda3 253:1 0 4G 0 part
vdb 253:0 0 2000G 0 disk
After connecting the Block Storage disk, a new disk vdX has appeared. This is your Block Storage disk. Replace X by the letter of your Block Storage disk (b in this example) in the examples in the rest of this article.
Please note: step 2-3 overwrite existing partitions and file systems on your Block Storage! Only perform these steps if the disk has been erased, or hasn't been partitioned yet.
Proceed to step 4 if you do NOT want to overwrite existing partitions and file systems and connect an existing Block Storage to another server, or if your VPS has been reinstalled again.
Step 2
The disk must be partitioned before you can install a file system. Use the following command to do so:
parted -s --align optimal /dev/vdX -- mklabel gpt mkpart primary 4MiB 100%Debian and Ubuntu often come without parted installed. If this is the case you can install it using the command:
apt-get install parted
Step 3
You can now create a file system. Below we're creating an ext4 file system, but you're welcome to choose xfs or btrfs should you prefer. These are out of the scope of this guide however.
mkfs -t ext4 /dev/vdX1
Step 4
Now mount the Block Storage disk and add it to /etc/fstab using the following commands:
mkdir /mnt/bigstorage
echo "/dev/vdX1 /mnt/bigstorage ext4 defaults 0 0" | tee -a /etc/fstab
mount /mnt/bigstorage
df -h | grep bigstorageIf succesful, you'll see a line after the last command which looks similar to:
/dev/vdb1 2.0T 33M 2.0T 1% /mnt/bigstorage
Step 5
Finally, test if you can write to your Block Storage disk:
touch /mnt/bigstorage/testfile && rm /mnt/bigstorage/testfile
You're now finished with this guide and ready to start using your Block Storage!




