In this article, we explain how to set an CNAME record within the DNS settings of your domain name.
CNAME stands for Canonical name. With this type of record, you can point a subdomain to another (sub)domain. A common application of a CNAME record is to have the www version of your website (e.g. www.example.com) point to the website on your primary domain (e.g. example.com).
Where do I add a CNAME record?
You can add all your DNS records easily and free of charge via your control panel. Go to 'Domain' and select the domain in the left column for which you want to set the CNAME record (don't check the box).
Now scroll to 'Advanced Domain Settings', followed by 'DNS'. If you do not see this yet, first click the switch behind 'TransIP settings' so the TransIP settings are switched off. The DNS records of your domain name will become visible, after which you can change them at will.
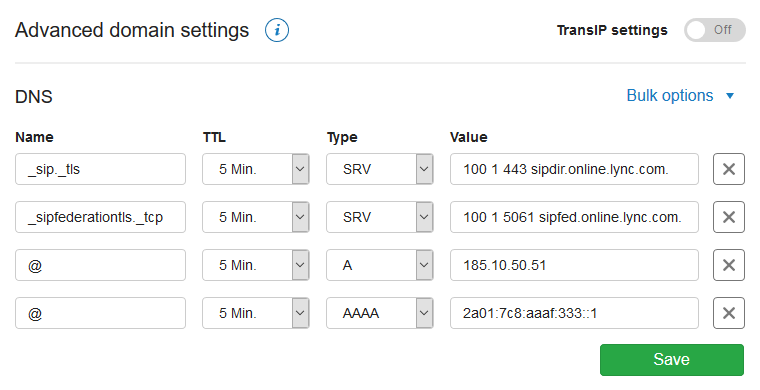
How do I set a CNAME record?
In the example below, you see an A record and a CNAME record for the site-example.com domain.
- The A record has an @ as a name and points to the IP address of the TransIP 'Reserved' page. The @ stands for the root domain (site-example.com).
- The CNAME record uses 'www' as the name and points to the root domain with an @.
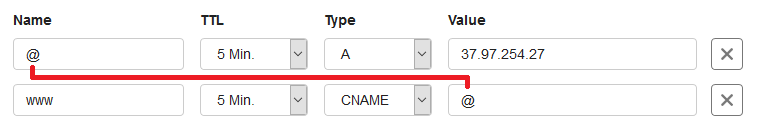
This way, visitors of www.site-example.com will be directed to the exact same address as visitors of the root domain.
Name
You set a CNAME record by starting with the name. As mentioned, you can only use a CNAME record for subdomains.
The 'Name' field is where you enter a subdomain. You do not have to add the root domain here; our DNS software automatically adds the root domain to the name in the background.
TTL
The 'TTL' of a DNS record determines how long the record can remain in the cache. We recommend keeping the TTL low, for example at 1 or 5 minutes.
Type
Because you want to set an CNAME record, choose 'CNAME' under 'Type'.
Value
The 'Value' is where you enter the (sub)domain where your subdomain should point to.
- If the subdomain should point to the same location as the root domain, use an @ as the value.
- If the subdomain should point to a different subdomain of the same domain name, only enter the subdomain as the value. You do not need to add the root domain here; our DNS software automatically adds the root domain to the name in the background.
- IMPORTANT! Web Hosting services at TransIP can only be used by the domain names they are ordered for. Because of this, you cannot point a CNAME record to a different domain name at TransIP when it is actively using a Web Hosting service.
- Want to point a CNAME record to a (sub)domain other than the domain you are setting the CNAME record for? Then make sure you enter the full (sub)domain in the 'Value' field and close the value with a dot. This so called 'trailing dot' prevents our DNS software of automatically adding the current root domain in the background.
Take note: The trailing dot can only be used for the value of CNAME, ALIAS, MX, and SRV records.
A trailing dot cannot be used for any DNS type when entering the 'Name' of a DNS record. The name can only consist of either the root domain (by entering an @) or a subdomain (by only entering the subdomain).
Keep in mind that it can take up to 24 hours before changes to DNS settings to be implemented globally. This is related to the way external systems process these changes. You usually see these changes well within 24 hours.
This article has discussed the setting of an CNAME record. For a general explanation about DNS records and how to set them, see the article ‘DNS and nameservers'.
If you want to know more about setting DNS records for your Web Hosting service, use the article 'The DNS settings of my web hosting package'.




